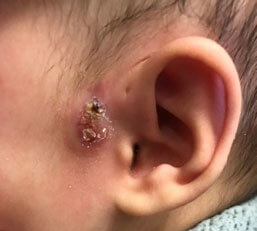
Preauricular sinus/cysts are caused by an embryological hillocks fusion abnormality when the outer ear is formed around 8-12 week intrauterine life. It is a common problem in many individuals and is estimated that up to 3% of the population may have the sinuses in the upper part of the ear (superior part of the auricle). The sinuses are blind-ending pockets which connect to the deeper part of the ear canal. The tract can produce debris, mucus and flaking squamous material from the skin lined epithelium, and this has the potential for infection when the sinuses are blocked. Majority of these sinuses do not need any intervention and can often go unnoticed.
In some young children and in the adolescent population the preauricular sinus can become infected and either cause a cyst formation or abscess. In most instances surface cleaning of the sinus, opening and clearing any blockage or if infected treating with antibiotics may be sufficient to prevent further flare-ups of infections. Frequently these infections/ abscesses may need drainage. This may require a general anaesthetic to drain the abscess. It is well accepted that once you have had one of these infections, it is more likely you will have infective episodes in future (50% chance) therefore we would usually advise removing the sinuses to prevent further infections and long term cosmetic deformity due to repeated infections, abscess formation and old incision and drainage scars.
Surgical removal is straight forward and is performed under a general anaesthetic, takes approximately 45 -60 minutes. This is usually a day-stay procedure. Risks related to the surgery are minimal as there are no major structures around this area apart from some small vessels but complications such as haematoma (blood clot at the site of surgery), secondary infection, and wound healing dehiscence can occur.
However, not too infrequently other cysts/lumps can present in this vicinity which can be misdiagnosed as a simple preauricular cyst or preauricular sinus infection. Other common lesions in this area include Dermoid cyst, Parotid cyst or tumours, Pilomatrixomas, MAIC (non-tuberculous -mycobacterial avian intraccellure complex) infection, keloid scar secondary to ear piercing and Lymphatic /vascular lesions (especially in young children). Further diagnostic work up include an initial assessment by an experienced Paediatric ENT surgeon with Ultrasound or MRI scanning. Fine needle aspiration is not always possible in children and is not recommended as an initial investigation. A good clinical assessment is the key in terms appropriate investigation and long term outcome for these patients.
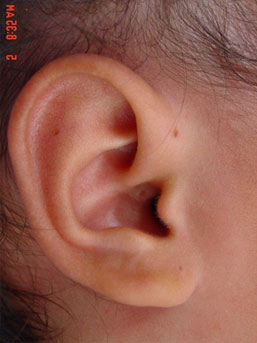
Non infected pre auricular sinus
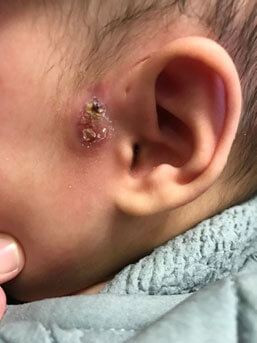
Infected Pre auricular sinus with abscess
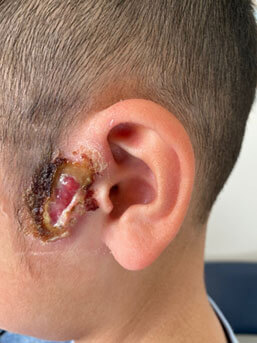
Pre auricular sinus with skin infection
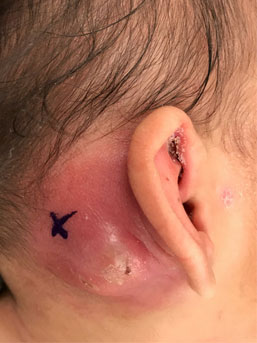
Post auricular abscess